A consortium of 19 partners is demonstrating new hydropower technologies in locations across Europe as part of the Hydropower Extending Power System Flexibility (XFLEX HYDRO) project.
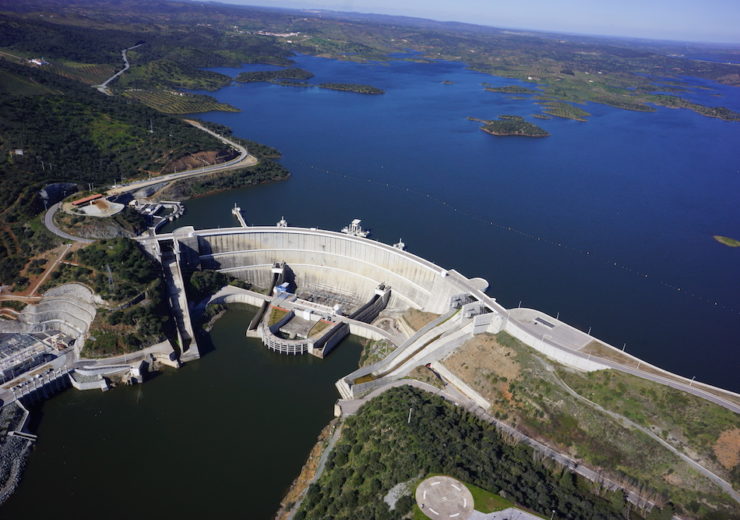

Alqueva was built in two phases totalling 520MW in Portugal. Credit EDP
XFLEX HYDRO is an ambitious energy innovation project launched across Europe to demonstrate how flexible hydropower technologies can deliver a low-carbon, secure and resilient power system.
By 2030, EU targets call for at least 32% of energy to be provided by renewables, with longer term scenarios suggesting an even more drastic decarbonisation of electricity by 2050.
Such demands will increase pressure on the hydropower sector to provide flexible, reliable power services that can adapt to changing supply and demand.
There will be an even greater need for new and innovative technologies to help hydro adjust to its critical role integrating variable renewables into the system, as well as to ensure hydropower operators can maximise their performance and access future energy markets.
XFLEX HYDRO and energy innovation
In an effort to demonstrate how smart hydropower technologies can deliver a low-carbon, reliable and resilient power system, a major new energy innovation project was launched in December 2019.
The €18 million initiative was announced by the European Commission at the United Nations climate change conference (COP25) in Madrid, Spain.
Awarded to a consortium of 19 organisations representing leading utilities, equipment manufacturers, universities, research centres and consultancies, it will show how hydro systems can help countries across the world meet their renewable energy targets.
The Hydropower Extending Power System Flexibility (XFLEX HYDRO) project is a four-year initiative and will demonstrate how modern hydropower plants can provide the vital power grid services required by variable renewables such as wind and solar power.
Patrick Child, Deputy Director-General for the European Commission’s Directorate-General Research and Innovation, commented: “Combining the excellence and expertise of 19 partners from across Europe, the XFLEX HYDRO project will test innovative solutions based on renewable energy sources that will provide greater flexibility and sustainability to the energy system.
“The project aims to increase hydropower’s potential in terms of plant efficiency, thereby boosting electrical power systems and enabling plant and system operators to operate more successfully in electricity markets. This can make an impactful contribution to European renewable energy objectives and policies.”
UN Emissions Gap Report
The launch comes after a major UN Emissions Gap Report looking at ways to reduce global carbon emissions was published in November 2019, and said that greater power system flexibility was “key” to integrating larger shares of variable renewable energy into the power supply.
“We need to decarbonise the power sector, and fast, if we are to limit the devastating impacts of climate change. The UN Emissions Gap Report is a stark reminder that we need hydropower to boost the contribution of variable renewables like wind and solar,” Eddie Rich, Chief Executive of the International Hydropower Association (IHA), which is responsible for XFLEX HYDRO project communications, said.
“The XFLEX HYDRO initiative represents a clear commitment by the European Commission, leading organisations from the hydropower sector and academia to invest in new and innovative hydropower technologies.”
XFLEX HYDRO is a four-year project
Over the next four years XFLEX HYDRO technologies to be tested are enhanced variable- and fixed-speed turbine systems, smart controls and a battery-turbine hybrid.
These will be demonstrated at the following seven hydropower plant sites across Europe:
- Z’Mutt in Switzerland.
- Grand Maison and Vogelgrün in France.
- Frades 2, Alqueva, Alto Lindoso and Caniçada in Portugal.

The project will conclude in 2023 by delivering a roadmap to increase adoption of the technologies across the hydropower fleet, with policy and market recommendations for governments, regulators and industry.
Professor François Avellan of EPFL, the research institute and university leading the project, stated: “Across Europe countries are embracing large-scale electricity generation from renewables such as solar and wind power and shifting away from conventional fossil fuels for electricity generation.
“The growth in variable renewables is changing how power grids operate, with potential impacts on the stability and security on the whole power grid. This places unprecedented challenges on the hydropower sector to provide flexible and reliable services to the grid.
“The technologies demonstrated by the XFLEX HYDRO project will help hydropower to consolidate its critical role to support the integration of variable renewables into the power grid. This will ensure hydropower operators can maximise their performance and access future energy markets,” he added.
The initiative has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.

XFLEX HYDRO project partners – Who’s who?
EPFL – Science and technology institution Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) is based in Switzerland and is the project leader responsible for scientific supervision and developing a new smart power plant supervisor system technology through the XFLEX HYDRO project.
Alpiq – Swiss energy services provider Alpiq produces 4200GWh of electricity from hydropower each year in Switzerland. In the project, Alpiq leads the demonstrator at Z’Mutt, in Switzerland.
Andritz AT – ANDRITZ HYDRO GmbH is a global supplier of electromechanical systems and services for hydropower plants. The company is a leader in the world market for hydraulic power generation. The company contributes to the demonstration in the Vogelgrün power plant focusing on optimised control of the hydraulic system in combination with a battery.
Andritz CH will contribute to the demonstration at the Vogelgrün power plant, focusing on generating a digital twin of the plant, developing a generic method for data based, real-time assessment of wear and tear.
Armines – a private non-profit research and technological organisation performing research contractual activities and academic research training. The project activities of Armines are primarily focused on implementing advanced control strategies and forecasting tools, and in the coordinated control of battery energy storage systems and hydropower plants.
CEA – a French public body and the country’s largest technology research and development provider whose role is to transfer this know-how to the industry. CEA is responsible for the battery storage system that is hybridised with the hydropower turbine in the Vogelgrün power plant.
EDF – EDF Group is the world’s leading electricity company whose Hydro Division largely contributes to the 98% CO² free electricity in France, with a yearly average generation of 43.5TWh with its 600+ dams and 400 power plants. EDF is responsible for two demonstrations in the project at Grand Maison and Vogelgrün power plants.
EDP CNET – EDP Centre for New Energy Technologies (EDP CNET) has the mission to create value through collaborative R&D in the energy sector. EDP CNET is responsible for two demonstrations within XFLEX (Alqueva and Alto Lindoso power plant in Portugal), and leads the definition of business use cases for the provision of flexibility services in the power system.
EDP P – EDP Gestão da Produção da Energia, S.A has some 1000 workers, with an installed capacity of 10GW, 6.7GW of which is hydropower (approximately 2.5 GW of which with pumping capacity). As a key utility partner and major hydro operator, EDP P provides the perspective of a large-scale storage investor/owner and is responsible for the Frades 2 demonstrator in Portugal.
GE Renewable Energy – Combines one of the broadest portfolios in the renewable energy industry to provide end-to-end solutions for customers demanding reliable and affordable green power. Its hydro activity group leads the development of solutions to extend flexibility services on three demonstrators: Grand Maison, Alqueva and Alto Lindoso power plants.
HES SO – HES SO is the largest university of applied sciences in Switzerland and its hydroelectric research group is in charge of the modelling, numerical analysis and prototype measurements in several demonstrators.
IHA – The International Hydropower Association (IHA) is a non-profit membership organisation committed to advancing sustainable hydropower by building and sharing knowledge on its role in renewable energy systems, responsible freshwater management and climate change solutions. IHA is responsible for XFLEX HYDRO project communications.
INESC TEC – A private non-profit institution leads the development and population of the hydro flexibility matrix, as well as the development of system integration studies and models for the technologies and solutions to attain the enhanced flexibility range.
PVE – Power Vision Engineering is a spin-off company of EPFL. Founded in 2007 it provides software solutions and expertise in the field of hydropower plant transient and dynamic behaviour. PVE contributes to the modelling and simulation of hydraulic and hydroelectric systems and is a supplier of the HydroClone innovative Real-Time Simulation Monitoring system.
SuperGrid Institute – SuperGrid Institute is an independent research and innovation centre that works to facilitate the wide-scale integration of renewable resources into the electrical grid. The institute is responsible for illustrating the impact of the flexible technologies and is developing a tool (Flexbot) to demonstrate their economic benefits. Its real-time hydraulic test platform will also be used to demonstrate the effectiveness of new flexible solutions.
UPC – Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya is a public institution dedicated to higher education and research, specialised in the fields of architecture, engineering and technology. UPC is responsible for the field tests and the installation of the monitoring system in the demonstrators.
USTUTT – The University of Stuttgart is responsible for the unsteady numerical flow field simulations to determine unsteady dynamic loads on pump-turbine components.
Voith Hydro – A global technology company whose hydro experts will focus on the development and implementation of additional solutions to make the Frades 2 demonstrator even more efficient, to increase its performance range, as well as to optimise its maintenance in order to strengthen its supportive role for the flexibility of the power system.
Zabala – is a Spanish company with wide experience in supporting organisations in the management of their research, technology development and innovation activities. Zabala participates in the definition of the business development plan for all knowledge created in the project and establishing a strategy for the protection of intellectual property.
XFLEX HYDRO demonstration sites
Alqueva, Portugal
Alqueva is a pumped storage scheme in southern Portugal that was built in two phases, Alqueva I and II, now totalling 520MW. The first station was operational in 2004 and the second commissioned more recently in 2017, each installed with two reversible Francis pump-turbines. At the site, the XFLEX HYDRO project aims to use hydraulic short circuit, extended operating range and optimised control to improve the flexibility provided to the grid – not only in terms of frequency services, but also voltage support.
Alto Lindoso, Portugal
Alto Lindoso is a 63MW hydropower plant situated on the Lima river in Portugal, installed with a 110m tall dam impounding its reservoir. Commissioned in 1992, the site represents a conventional hydro plant including two Francis turbines designed for high head (pressure) and power generation (without pumping). In XFLEX HYDRO, low cost opportunities to extend operating range and optimise power flexibility will be tested at the plant, and compared to the variable speed case.
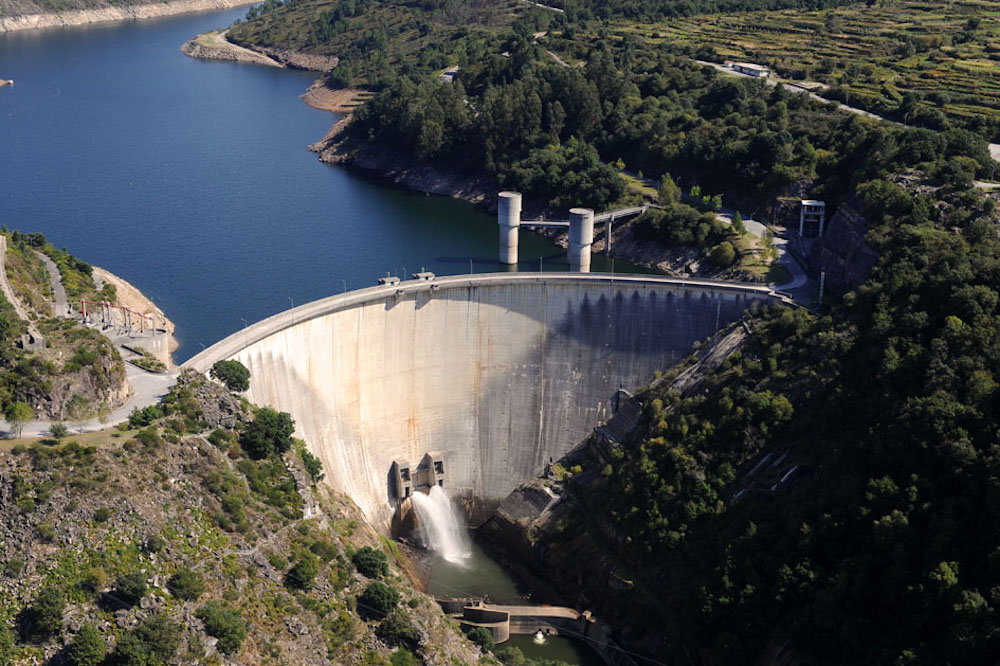

Caniçada, Portugal
Caniçada is a 62MW hydropower plant with reservoir storage located in northern Portugal, originally commissioned in 1954 and more recently refurbished in 2017/2018. With two generating units rated at medium head and power generation, the aim for Caniçada in XFLEX HYDRO is to evaluate flexibility opportunities for medium scale hydro and, in particular, simulate potential conversion to variable speed.

Frades 2, Portugal
Frades 2 is a new 780MW pumped storage hydropower plant in northern Portugal. Commissioned in 2017, the two generator sets are the largest and most powerful of their kind in Europe. Under XFLEX HYDRO, the site will demonstrate an innovative operating regime: hydraulic short circuit operation using variable speed units and smart controls to optimise power services onto the grid network, focusing on fast frequency services.
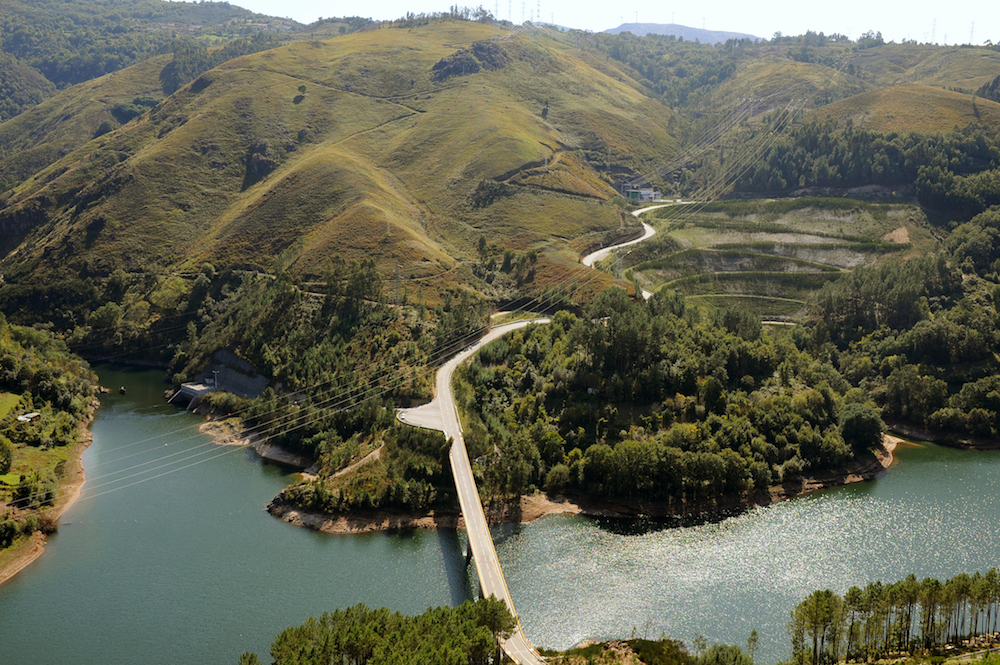

Grand Maison, France
Sitting in the French Alps, Grand Maison is Europe’s largest pumped storage plant at 1800MW capacity. The plant has multiple production units including four Pelton turbines and eight reversible pumps, which first went into service in 1986. During the XFLEX HYDRO project, hydraulic short circuit will be demonstrated using new turbine runners and automation techniques for advanced control and efficiency.
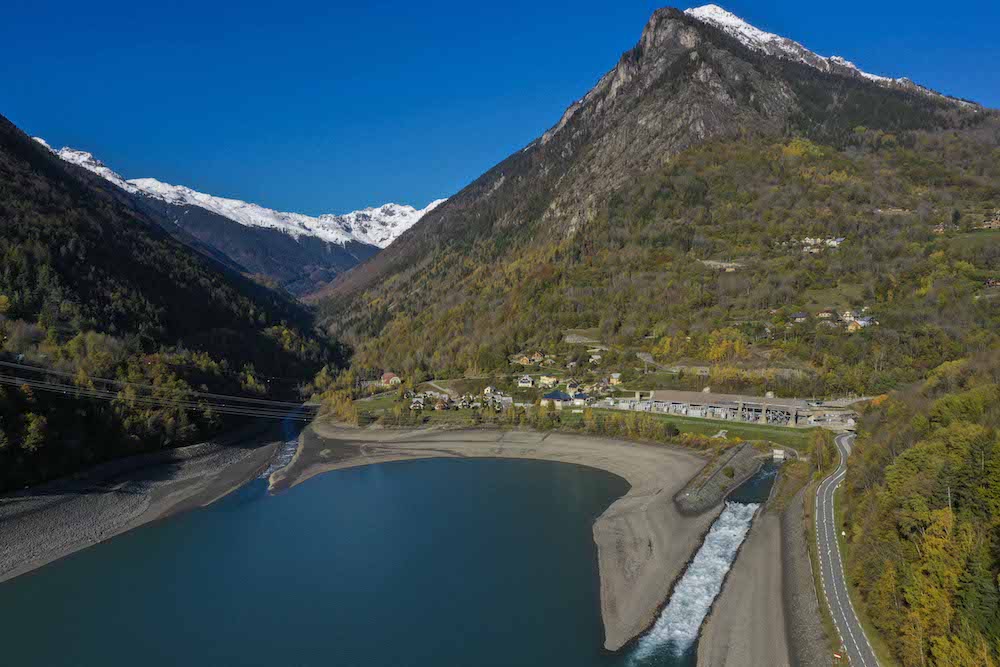

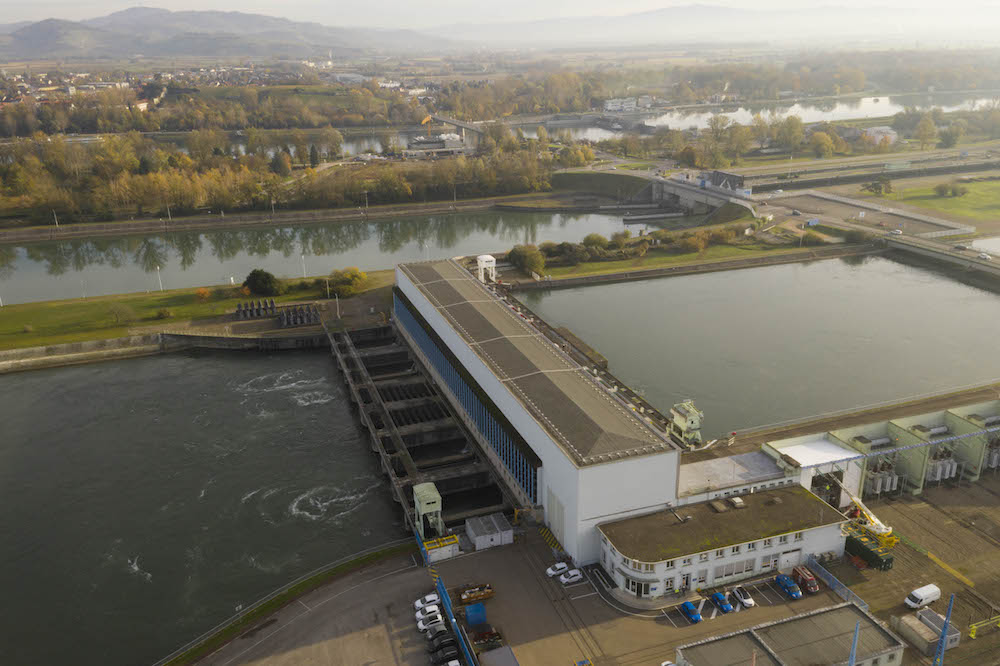
Vogelgrun, France
Vogelgrun is a 142MW run-of-river hydropower plant in France, situated near the border with Germany along the river Rhine. The plant has four low head Kaplan turbines, in service since 1959, and during XFLEX HYDRO one of the units will be hybridised with a battery. Complementing the turbine’s operations, the battery system will add energy storage to share response capability with the hydraulic unit, and use a master control to optimise both flexibility and wear and tear effects.
Z’Mutt, Switzerland
Z’Mutt is a pumping station located in Canton Valais, Switzerland, and feeds water into the main reservoir of the Grande Dixence hydroelectric scheme. Originally commissioned in 1964, Z’Mutt has a total pumping capacity of 88MW across five existing pumps. During XFLEX HYDRO, one unit will be replaced with a new 5MW variable speed reversible pump-turbine which, when installed with modern power electronics and smart controls, will demonstrate a high range of flexibility.
