The Cerro Del Gallo project is a gold-copper-silver deposit located 30km east of Guanajuato City, in central Mexico.
Originally owned by Primero Mining, the Cerro Del Gallo project was acquired by Argonaut for $15m through the purchase of all issued and outstanding shares of Primero’s subsidiary, San Anton Resource Corporation, in November 2017.
A definitive feasibility study was conducted by Primero in May 2012, while a new exploration study was initiated by Argonaut upon the acquisition of the project. The results of the Cerro Del Gallo pre-feasibility study (PFS) was announced in December 2019.
The project is expected to require an investment of approximately $184.6m (£141.2m). It is estimated to have a life of 15.5 years with the probability of extension based on future explorations.
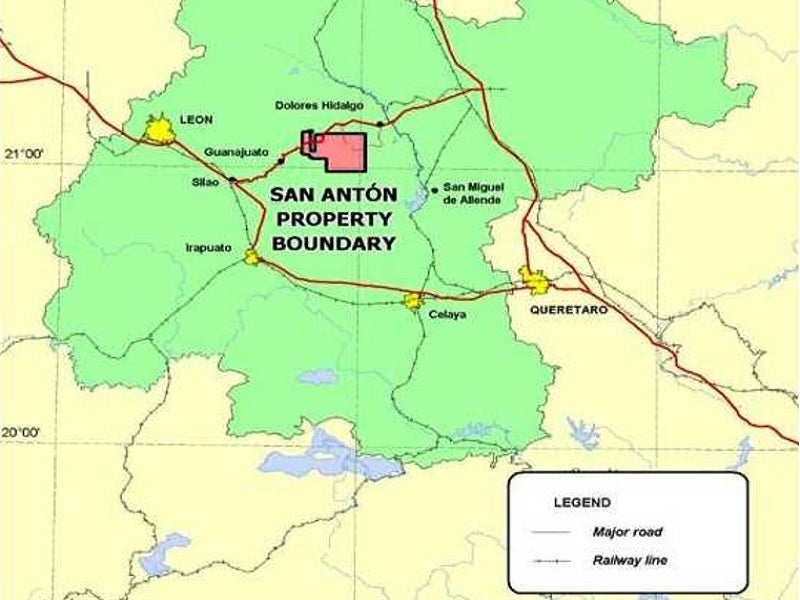
Cerro Del Gallo project location and geology
The Cerro Del Gallo deposit is located within the San Antón property which includes 13 granted mining concessions.
The site is accessible year-round via a good network of local roads and tracks. It is primarily connected to the sealed Federal Highway 110 through a 17km-long, all-weather gravel road. Rail services are also available within 20km distance of Cerro Del Gallo. The nearest airport to the site is Guanajuato International Airport, which is located just 30km away from Cerro Del Gallo.
Cerro Del Gallo lies within the Mesa Central physiographic province at the intersection of the Sierra Madre Oriental and the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt geological provinces.
The oldest rocks found in the area are a deformed and regionally metamorphosed volcano-sedimentary sequence from Triassic to Cretaceous age. The Esperanza Formation in the area contains encrusted sediments of argillaceous, silty argillaceous and arenaceous structure, and fragmental volcanic rocks.
Mineral reserves of Cerro Del Gatto
As of December 2019, the proven and probable reserves of the Cerro Del Gallo project were estimated to be 91.8Mt grading at 0.56g/t Au, 13.3g/t Ag and 0.09% Cu.
Mining at Cerro Del Gatto project
The project will employ an open-pit mine design with truck and shovel operation. The mining fleet is expected to include 91t haul trucks and 12cm3 front-end loaders with a strip ratio of 0:63.
Mined ore will be trucked directly to the crusher facility for crushing by cone and high-pressure grinding rolls (HPGR) crushers. In the event of any unexpected crusher downtime, a small stockpile may be maintained near the crusher.
This will allow the trucks to dump the ore loads and return to mining operations. The total mine throughput is expected to be approximately 6Mt a year.
Cerro Del Gatto ore processing
Ore is estimated to contain an average of 0.09% copper with portions of cyanide soluble content which is expected to be extracted in the heap leach circuit.
A sulfidation, acidification, recycle, and thickening (SART) plant will be installed for copper removal and cyanide recovery. The plant will release cyanide associated with the copper cyanide complex and will recycle it back for use in the leach process. The process also yields copper and silver precipitate which will be sold to bring additional revenue to the project.
A dilute cyanide solution will be used to leach the ore at high application rate for the first 40 days, while a lower application rate will be used for the remaining 80 days of the 120-day leach cycle. The pregnant solution containing gold, silver, and copper will be collected in a pond and pumped to the SART plant.
The pregnant solution will undergo acidification with sulfuric acid for producing copper and silver precipitate in the form of sulphides through the addition of sodium hydrosulphide. The precipitate will be thickened and filtered to produce a copper-silver filter cake for delivery to a smelter.
Gold will be recovered from the copper stripped barren solution in the SART plant by processing it in a carbon adsorption-desorption-recovery (ADR) plant. It will be plated on stainless steel cathodes which will be removed by washing. The solution will then be filtered, dried and smelted to produce dore bars.
Contractors involved
Kappes Cassiday & Associates (KCA) provided engineering and design of the processing plant for complete crushing, leaching, and recovery systems.
MC Terra prepared a technical document for land-use change, while metallurgical testing was conducted by KCA.