
In 2018, global LNG trade reached 316.5 million tonnes, according to the 2019 World LNG Report prepared by the International Gas Union (IGU). The number of LNG exporting markets increased to 19 last year, with 2.4 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) Kribi FLNG project coming online in Cameroon.
NS Energy profiles the list of the top five LNG exporting countries in 2018
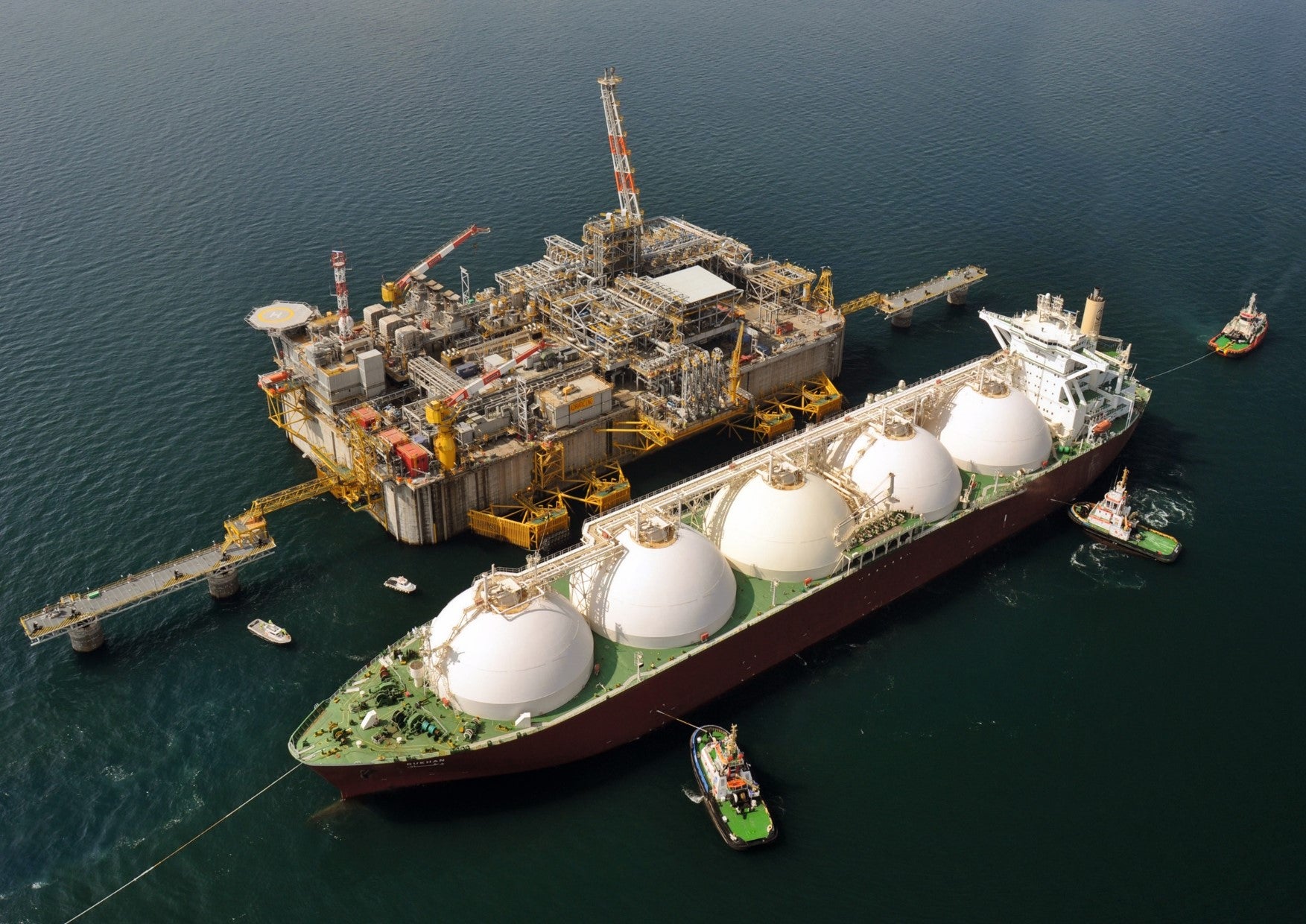
Qatar – 104.8bcm
Qatar is the largest exporter of LNG in the world. The country’s LNG exports stood at 104.8 billion cubic metres (bcm) last year, according to the BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2019. The Doha-headquartered Qatargas is the world’s largest LNG producing company. Its offshore operations are located approximately 80km northeast of Qatar mainland.
The company produces approximately 18.5 billion standard cubic feet per day (bscfd) of sour gas from a total of 208 wells and then supplies to 14 LNG trains and four sales gas trains onshore. The gas, along with the associated condensate, is then transferred via subsea pipelines to shore.
Qatargas also operates the North Field Bravo (NFB) and RasGas Alfa (RGA) offshore complexes which account for nearly 2.8bscfd of dry gas to its total offshore gas production.
State-owned petroleum company Qatar Petroleum operates what it claims to be the largest single non-associated gas reservoir in the world, North Gas Field. Discovered in 1971, the field is estimated to have a total recoverable gas of more than 900 trillion standard cubic feet (tscf).
Qatar also plans to increase its LNG exports capacity by 43% and develop its North Field Expansion project, adding about 32mtpa of liquefied gas to the market from 2024.
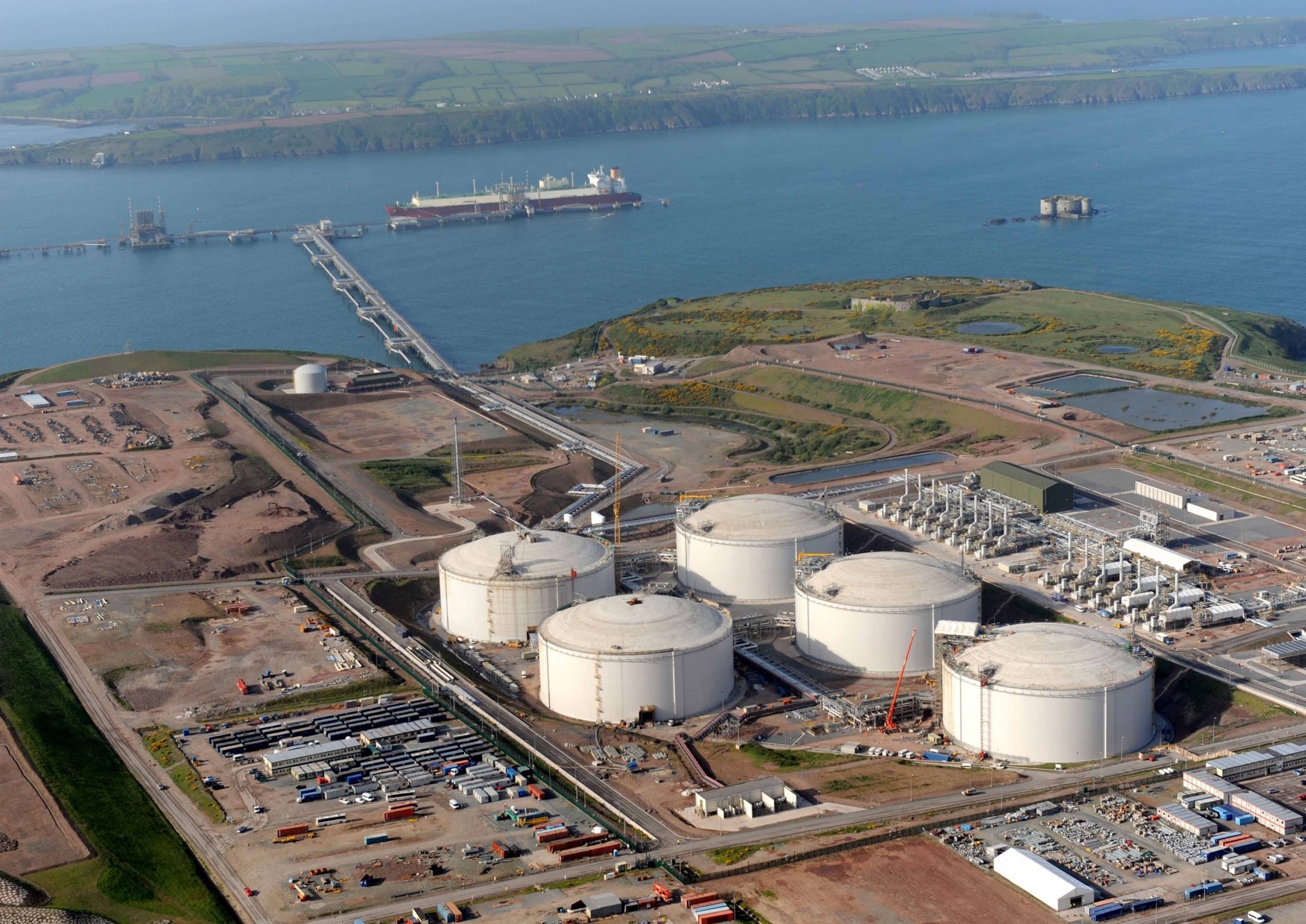

Australia – 91.8bcm
With LNG exports of 91.8bcm last year, Australia stands at the second spot in the list. The country operates one of the world’s biggest LNG projects, the Ichthys LNG, which involved the development of Ichthys gas-condensate field located approximately 220km offshore Western Australia.
The Ichthys LNG project is owned by its operator INPEX (62.245%), Total (30%), CPC Corporation Taiwan (2.625%), Tokyo Gas holding (1.575%), Osaka Gas (1.2%), Kansai Electric Power (1.2%), JERA (0.735%) and Toho Gas (0.42%).
According to estimates, the offshore field is estimated to contain more than 12.8 trillion cubic feet of gas and 500 million barrels of condensate at depth up to 4,500m beneath the seabed.
The country also operates the world’s biggest FLNG facility, Prelude FLNG project located in the Browse Basin offshore Western Australia. The FLNG facility has the capacity to produce 5.3 million tonnes of liquids and condensate a year, including 3.6mtpa of LNG, 1.3mtpa of condensate, and 0.4mtpa of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
Some of the other LNG projects in the country include the Wheatstone LNG facility, the Arcadia gas project, and the Gorgon LNG project.
Malaysia – 33bcm
Malaysia occupies third place in the list, with LNG exports of 33bcm in 2018. The country operates PETRONAS LNG Complex, an integrated LNG production complex and one of the world’s largest LNG production facilities in a single location.
With nine production trains, the PETRONAS LNG Complex has a production capacity of 29.3mtpa. PETRONAS Floating LNG (PFLNG) is another major facility that enables the processing of LNG to be carried out offshore. The PFLNG Satu is currently operating at Kanowit gas field, offshore Sarawak, while PFLNG Dua, the second floating LNG facility, is expected to be completed by 2020.
The country also operates Beryl Gas Field located in Block SK10 off the shore of Sarawak, Malaysia, near the Helang gas field and Layang oil field that are located within the same block.
Malaysia is also set to commence production from the Pegaga gas field, located in 108m of water in Block SK320 off the shore of Sarawak, in 2021. In July 2019, PTT Exploration and Production Public Company (PTTEP) discovered a large gas field with its first well on the SK410B block offshore Sarawak, Malaysia.
US – 28.4bcm
The US stands fourth in the list of top LNG exporting countries with an exporting capacity of 28.4bcm. The North American nation contributed to 6.7% of the world’s LNG exports in 2018. As of May 2019, the country has more than 110 LNG facilities in operation, carrying out a range of services, of which some of them export the commodity to other countries.
Some of the existing LNG export facilities in the US are the Sabine Pass LNG Terminal (3.5bcfd) in Louisiana, Cove Point LNG Terminal (0.82bcfd) in Maryland, Corpus Christi Liquefaction Project (0.71bcfd) in Texas, Cameron LNG project (0.71bcfd) in Louisiana, and Kenai LNG plant (0.2bcfd) in Arkansas.
The Sabine Pass LNG Terminal, which is being developed by Cheniere Energy, will have a total of six liquefaction trains to deliver nearly 27mtpa of LNG.
The LNG export capacity of the US is set to increase through at least eight LNG export terminals, which have been approved and are under construction. Additionally, there are quite a few LNG projects, which have been approved but are yet to break ground.
By 2021, six LNG projects are slated to become fully operational, while two new projects, the Golden Pass LNG export project in Texas and Calcasieu Pass LNG project in Louisiana are scheduled to begin operations by 2025.
Russia – 24.9bcm
At the fifth position among the top LNG exporting countries is Russia with an export capacity of 24.9bcm. A bulk of its production comes from the Yamal LNG Project and Sakhalin II, which became the first LNG plant to be commissioned in Russia when it came online in 2009.
Russia contributed 6% of the total LNG exports in 2018.
The £22bn Yamal LNG Project, which is located in the Yamal Peninsula, has an output capacity of nearly 16.5mtpa. Stakeholders of the three-train LNG project are Novatek (50.1%), Total (20%), CNPC (20%) and Silk Road Fund (9.9%).
Yamal LNG, which began operations in late 2017, sources gas produced from the South Tambey Field. Sakhalin II, which is located in the Sakhalin Island in the Russian Far East, has a design capacity of 9.6mtpa produced from two liquefaction trains. In 2018, the Sakhalin II LNG plant produced 11.41 million tonnes of LNG.
In April 2019, Novatek and Gazprombank Cryogas-Vysotsk commenced full-scale production from the Cryogas-Vysotsk LNG project in the Leningrad Region. Cryogas-Vysotsk, which has an initial design capacity of 660 thousand tons of LNG per annum, supplies the commodity to northern European countries, Scandinavia and the Baltic Region, apart from serving the domestic market.
Russia’s LNG export capacity is set to increase further by the Arctic LNG 2 project, which is being built by Novatek and Ekropromstroy in the Gydan peninsula with an investment of nearly $21-23bn (£17.19-18.8bn). Scheduled to be commissioned in 2023, the Arctic LNG 2 project will have a capacity of 19.8mtpa.






